Back Procedures Explained
Disclaimer:
This website is intended to assist with patient education and should not be used as a diagnostic, treatment or prescription platform or service. Always refer any concerns or questions about diagnosis, treatment or prescription to your doctor.
Intravenous Pyelogram (IVP)
We have selected the following expert medical opinion based on its clarity, reliability and accuracy. Credits: Sourced from the website Healthwise, authored by Healthwise Staff (see below). Please refer to your own medical practitioner for a final perspective, assessment or evaluation.
What is an IVP?
An intravenous pyelogram (IVP) is an X-ray test that provides pictures of the kidneys, the bladder, the ureters, and the urethra (urinary tract). An IVP can show the size, shape, and position of the urinary tract, and it can evaluate the collecting system inside the kidneys.
During IVP, a dye called contrast material is injected into a vein in your arm. A series of X-ray pictures is then taken at timed intervals.
IVP is commonly done to identify diseases of the urinary tract, such as kidney stones, tumours, or infection. It is also used to look for problems with the structure of the urinary tract that were present from birth (congenital).
An ultrasound or a computed tomography (CT) scan may be combined with an IVP if more details about the urinary tract are needed. A computed tomography intravenous pyelogram (CT/IVP) is usually done to look for the cause of blood in the urine.
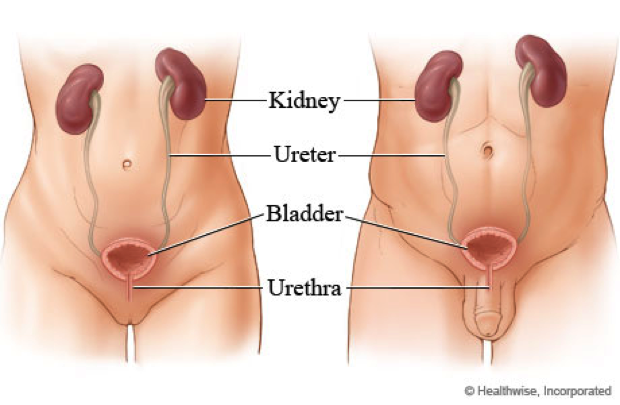
The Urinary Tract
The kidneys and bladder work together to make urine and remove it from your body. The kidneys filter waste products and water from the blood to form urine. The urine moves from the kidneys through tubes called ureters to the bladder, which stores the urine until it is full. From the bladder, urine leaves the body through another thin tube, the urethra. After the bladder starts to empty, it normally empties all the urine.
Why an IVP is done
An intravenous pyelogram (IVP) is done to:
- Look for problems with the structure of the urinary tract.
- Find the cause of blood in the urine.
- Find the cause of ongoing back or flank pain.
- Locate and measure a tumour of the urinary tract.
- Locate and measure a kidney stone.
- Find the cause of recurring urinary tract infections.
- Look for damage to the urinary tract after an injury.
How to prepare for an IVP
Before having an intravenous pyelogram (IVP), tell your doctor if:
- You are or might be pregnant.
- You are breastfeeding. It's safe to breastfeed your baby after you have had this test. The amount of dye that gets into your breast milk is tiny and will not harm your baby.
- You have an intrauterine device (IUD) in place.
- You are allergic to the iodine dye used as the contrast material for X-ray tests or to anything else that contains iodine.
- You have ever had a serious allergic reaction (anaphylaxis), such as after being stung by a bee or from eating shellfish.
- Within the past 4 days, you have had an X-ray test using barium contrast material (such as a barium enema).
- You have had kidney problems in the past or have diabetes, especially if you take metformin (Glucophage) to control your diabetes. The contrast material used during an IVP can cause kidney damage in people who have poor kidney function. If you have had kidney problems in the past, blood tests (creatinine, blood urea nitrogen) may be done before the test to make sure that your kidneys are working properly.
You may need to stop eating and drinking for 8 to 12 hours before the IVP. You also may need to take a laxative the evening before the test (and possibly have an enema the morning of the test) to make sure that your bowels are empty.
This test is often done in children to see if they may have an abnormal backflow of urine (vesicoureteral reflux). Prepare your child for exams and tests that are needed. Explain them in a simple way. Use positive words as much as possible. Doing so will help your child understand what to expect and can help reduce fears.
Talk to your doctor about any concerns you have regarding the need for the test, its risks, how it will be done, or what the results will mean.
How an IVP is done
An intravenous pyelogram (IVP) is usually done by a radiology technologist. The IVP pictures are interpreted by a doctor who specializes in interpreting imaging tests (radiologist).
You will need to remove any jewellery that might interfere with the X-ray picture. You will need to take off all or most of your clothes, and you will be given a cloth or paper covering to use during the test. You will be asked to urinate just before the test begins.
During the test
You will lie on your back on an X-ray table. An X-ray picture of your belly will be taken and reviewed by the radiologist before the next part of the test begins.
The injection site on your arm will be cleaned and the contrast material will be injected into a vein on the inside of your elbow. The dye travels through the bloodstream, is filtered out by the kidneys, and passes into the urine. The urine then flows into the tubes (ureters) that lead to the bladder.
X-ray pictures are taken several minutes apart as the dye goes through the urinary tract. Each picture is developed right away. Sometimes more pictures are taken based on earlier ones. You may be asked to turn from side to side or to hold several different positions so the radiologist can take a complete series of X-rays.
During IVP, a compression device may wrapped around your belly to keep the dye in the kidneys. The most common compression device is a wide belt containing two inflated balloons that push in on either side of your belly to block the passage of dye through the ureters. If you have recently had abdominal surgery or have an abdominal disorder, the band will not be used.
A special type of X-ray technique called fluoroscopy may also be used during IVP. During fluoroscopy, a continuous X-ray beam is used to display a moving image on a video monitor.
IVP usually takes about an hour.
After the test
After the test is over, you will need to drink plenty of liquids to help flush the contrast material out of your body.
How an IVP feels
You will feel no discomfort from the X-rays. The X-ray table may feel hard and the room may be cool. You may find that the positions you need to hold are uncomfortable.
You will feel a brief sting when the needle is inserted into the vein in your arm. When the contrast material is injected, you may feel slight burning in your arm and flushing throughout your body. You may also notice a salty or metallic taste in your mouth.
The compression belt may feel tight. If it is painful, tell the technologist and ask that it be readjusted.
You may feel slightly weak, nauseated, or lightheaded for a short time after the test.
Risks
There is always a slight chance of damage to cells or tissue from radiation, including the low levels of radiation used for this test. But the chance of damage from the X-rays is usually very low compared with the benefits of the test.
There is slight risk of having an allergic reaction to the contrast material. The reaction can be mild (itching, rash) or severe (trouble breathing or sudden shock). Death resulting from an allergic reaction is very rare. Most reactions can be controlled with medicine. Be sure to tell your doctor if you have asthma or allergies of any kind, such as hay fever, iodine allergy, bee stings, or food allergies.
People with certain conditions (such as diabetes, multiple myeloma, chronic kidney disease, sickle cell disease, or pheochromocytoma) have increased chances of having sudden kidney failure from IVP. Older adults and people taking medicines that affect the kidney may also have increased chances for problems after an IVP.
IVP Results
An intravenous pyelogram (IVP) is an X-ray test that provides pictures of the kidneys, the bladder, the ureters, and the urethra (urinary tract). Your doctor may be able to talk to you about some results right away. Complete results are usually ready in 1 to 2 days.
Normal IVP results
- The kidneys, ureters, and bladder are normal in position, size, and shape.
- The contrast material reaches the kidneys in a normal amount of time.
- No blockage can be seen in the kidneys, ureters, or bladder.
- In men, the prostate gland looks normal in position, size, and shape.
Abnormal IVP results
- The kidneys, ureters, or bladder may be abnormal in position, size, or shape. A kidney may be absent, or an extra kidney or ureter may be present.
- The kidneys are too large or too small.
- The contrast material takes longer than normal to reach a kidney.
- An abnormal growth (such as a tumour), one or more cysts, an abscess, or a kidney stone is seen.
- A kidney is swollen with urine from a blockage such as a tumour or kidney stone.
- Injury to the kidney, ureter, or bladder is seen.
- The kidney contains scarring.
- In men, the prostate gland is too large.
What affects the test?
Reasons you may not be able to have the test or why the results may not be helpful include:
- Being unable to remain still during the test.
- Having a large amount of stool (faeces) or gas in the large intestine (colon).
- Having a recent test with barium (such as a barium enema).
An intravenous pyelogram (IVP) is not usually done for a pregnant woman because the X-rays could damage the growing baby. If a view of a pregnant woman's kidneys is needed, an ultrasound test may be done instead.
What to think about
A preliminary X-ray picture (KUB) of your abdomen will be taken before the intravenous pyelogram (IVP). This picture is reviewed by the radiologist before the next part of the test begins. An IVP test may not be done if these pictures show a problem.
Other tests that may be used instead of an intravenous pyelogram (IVP) include computerized tomography (CT scan), ultrasound, digital subtraction angiography, and, occasionally, MRI.
For people who have known kidney problems, diabetes, or who are dehydrated, steps may be taken to prevent kidney damage. Less contrast material may be used and additional fluids may be given before, during, and after the test.
If you have had kidney problems in the past, blood tests for creatinine and blood urea nitrogen may be done before the test to make sure that your kidneys are working properly.
Another test that may be done to look at the urinary tract is retrograde ureteropyelogram. Retrograde ureteropyelogram is done when IVP results do not help identify a problem or when IVP can't be done because of poor kidney function or an allergy to the iodine contrast material.
About the source
Healthwise Staff
Medical Reviewers:
- Gregory Thompson, MD - Internal Medicine
- Adam Husney, MD - Family Medicine
- Martin J. Gabica, MD - Family Medicine
Current as of October 09, 2017
References
- Chernecky CC, Berger BJ (2008). Laboratory Tests and Diagnostic Procedures, 5th ed. St. Louis: Saunders.
- Fischbach FT, Dunning MB III, eds. (2009). Manual of Laboratory and Diagnostic Tests, 8th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams and Wilkins.
- Pagana KD, Pagana TJ (2010). Mosby’s Manual of Diagnostic and Laboratory Tests, 4th ed. St. Louis: Mosby Elsevier.
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Are you a healthcare practitioner who enjoys patient education, interaction and communication?
If so, we invite you to criticise, contribute to or help improve our content. We find that many practicing doctors who regularly communicate with patients develop novel and often highly effective ways to convey complex medical information in a simplified, accurate and compassionate manner.
MedSquirrel is a shared knowledge, collective intelligence digital platform developed to share medical expertise between doctors and patients. We support collaboration, as opposed to competition, between all members of the healthcare profession and are striving towards the provision of peer reviewed, accurate and simplified medical information to patients. Please share your unique communication style, experience and insights with a wider audience of patients, as well as your colleagues, by contributing to our digital platform.
Your contribution will be credited to you and your name, practice and field of interest will be made visible to the world. (Contact us via the orange feed-back button on the right).
Disclaimer:
MedSquirrel is a shared knowledge, collective intelligence digital platform developed to share medical knowledge between doctors and patients. If you are a healthcare practitioner, we invite you to criticise, contribute or help improve our content. We support collaboration among all members of the healthcare profession since we strive for the provision of world-class, peer-reviewed, accurate and transparent medical information.
MedSquirrel should not be used for diagnosis, treatment or prescription. Always refer any questions about diagnosis, treatment or prescription to your Doctor.
