Back Conditions Explained
Airplane Ear
Also known as "Barotrauma of the Ear" and "Barotitus Media"
We have selected the following expert medical opinion based on its clarity, reliability and accuracy. Credits: Sourced from the website Mayo Clinic, Minnesota. Please refer to your own medical practitioner for a final perspective, assessment or evaluation.
Overview
Airplane ear is the stress exerted on your eardrum and other middle ear tissues when the air pressure in your middle ear and the air pressure in the environment are out of balance. You may experience airplane ear at the beginning of a flight when the airplane is climbing or at the end of a flight when the airplane is descending. These fast changes in altitude cause air pressure changes and can trigger airplane ear.
Airplane ear is also called ear barotrauma, barotitis media or aerotitis media.
Usually self-care steps — such as yawning, swallowing or chewing gum — can prevent or correct the differences in air pressure and improve airplane ear symptoms. However, a severe case of airplane ear may need to be treated by a doctor.
Symptoms
Airplane ear can occur in one or both ears.
Airplane ear signs and symptoms may include:
- Moderate discomfort or pain in your ear
- Feeling of fullness or stuffiness in your ear
- Muffled hearing or slight to moderate hearing loss
If airplane ear is severe or lasts more than a few hours, you may experience:
- Severe pain
- Pressure in your ear similar to being underwater
- Moderate to severe hearing loss
- Ringing in your ear (tinnitus)
- Spinning sensation (vertigo)
- Vomiting resulting from vertigo
- Bleeding from your ear
When to see a doctor
Usually you can do things on your own to treat airplane ear. If discomfort, fullness or muffled hearing lasts more than a few hours or if you experience any severe signs or symptoms, call your doctor.
Causes
Middle ear
The middle ear includes three small bones — the hammer (malleus), anvil (incus) and stirrup (stapes). The middle ear is separated from your external ear by the eardrum and connected to the back of your nose and throat by a narrow passageway called the eustachian tube. The cochlea, a snail-shaped structure, is part of your inner ear.
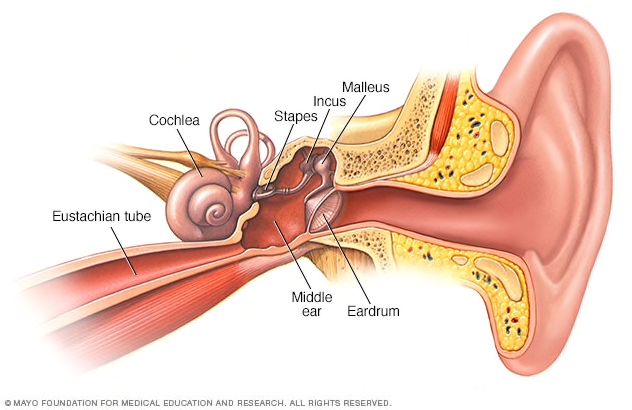
Airplane ear occurs when an imbalance in the air pressure in the middle ear and air pressure in the environment prevents your eardrum (tympanic membrane) from vibrating as it should. Air pressure regulation is the work of a narrow passage called the eustachian tube. One end is connected to the middle ear. The other end has a tiny opening where the back of the nasal cavity and the top of the throat meet (nasopharynx).
When an airplane climbs or descends, the air pressure in the environment changes rapidly, and your eustachian tube often doesn't react quickly enough. Swallowing or yawning activates muscles that open the eustachian tube and allow the middle ear to replenish its air supply, often eliminating the symptoms of airplane ear.
Ear barotrauma also may be caused by:
- Scuba diving
- Hyperbaric oxygen chambers
- Explosions nearby
You may also experience a minor case of barotrauma while riding an elevator in a tall building or driving in the mountains.
Risk factors
Any condition that blocks the eustachian tube or limits its function can increase the risk of airplane ear.
Common risk factors include:
- A small eustachian tube, especially in infants and toddlers
- The common cold
- Sinus infection
- Hay fever (allergic rhinitis)
- Middle ear infection (otitis media)
- Sleeping on an airplane during ascent and descent
Frequent or severe airplane ear may damage the tissues of the inner ear or eustachian tube, which increases your chances of experiencing the problem again.
Complications
Airplane ear usually isn't serious and responds to self-care. Long-term complications may occur when the condition is serious or prolonged or if there's damage to middle or inner ear structures.
Rare complications may include:
- Permanent hearing loss
- Ongoing (chronic) tinnitus
Prevention
Follow these tips to avoid airplane ear:
- Yawn and swallow during ascent and descent: Yawning and swallowing activate the muscles that open your eustachian tubes. You can suck on candy or chew gum to help you swallow.
- Use the Valsalva maneuver during ascent and descent: Gently blow, as if blowing your nose, while pinching your nostrils and keeping your mouth closed. Repeat several times, especially during descent, to equalize the pressure between your ears and the airplane cabin.
- Don't sleep during takeoffs and landings: If you're awake during ascents and descents, you can do the necessary self-care techniques when you feel pressure on your ears.
- Reconsider travel plans: If possible, don't fly when you have a cold, sinus infection, nasal congestion or ear infection. If you've recently had ear surgery, talk to your doctor about when it's safe to travel.
- Use filtered earplugs: These earplugs slowly equalize the pressure against your eardrum during ascents and descents. You can purchase these at drugstores, airport gift shops or your local hearing clinic.
- Use an over-the-counter decongestant nasal spray: If you have nasal congestion, use a nasal decongestant about 30 minutes to an hour before takeoff and landing. Avoid overuse, however, because nasal decongestants taken over several days can increase congestion.
- Use oral decongestant pills cautiously: Oral decongestants may be helpful if taken 30 minutes to an hour before an airplane flight. However, if you have heart disease, a heart rhythm disorder or high blood pressure, or if you've experienced possible medication interactions, avoid taking an oral decongestant unless your doctor approves. If you're a man older than age 50, you may experience serious side effects after taking decongestants containing pseudoephedrine (Actifed, Sudafed) such as urinary retention, especially if you have an enlarged prostate. If you're pregnant, talk to your doctor before taking oral decongestants.
- Take allergy medication: If you have allergies, take your medication about an hour before your flight.
If you're prone to severe airplane ear and must fly often, your doctor may surgically place tubes in your eardrums to aid fluid drainage, ventilate your middle ear, and equalize the pressure between your outer ear and middle ear.
Helping children prevent airplane ear
These additional tips can help young children avoid airplane ear:
- Encourage swallowing: Give a baby or toddler a beverage during ascents and descents to encourage frequent swallowing. A pacifier also may help. Have the child sit up while drinking. Children older than age 4 can try chewing gum, drinking through a straw or blowing bubbles through a straw.
- Consider eardrops: Talk to your child's doctor about prescribing your child eardrops that contain a pain reliever and numbing agent for the flight.
- Avoid decongestants: Decongestants aren't recommended for young children.
Diagnosis
Your doctor will likely be able to make a diagnosis based on questions he or she asks and an examination of your ear with a lighted instrument (otoscope). Signs of airplane ear might include a slight outward or inward bulging of your eardrum. If your condition is more severe, your doctor may see a tear in the eardrum or a pooling of blood or other fluids behind your eardrum.
If you're experiencing a spinning sensation (vertigo), there may be damage to structures of your inner ear. Your doctor may suggest a hearing test (audiometry) to determine how well you detect sounds and whether the source of hearing problems is in the inner ear.
Treatment
For most people, airplane ear usually heals with time. When the symptoms persist, you may need treatments to equalize pressure and relieve symptoms.
Medications
Your doctor may prescribe medications or direct you to take over-the-counter medications to control conditions that may prevent the eustachian tubes from functioning well.
These drugs may include:
- Decongestant nasal sprays
- Oral decongestants
- Oral antihistamines
To ease discomfort, you may want to take a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) or naproxen sodium (Aleve, others), or an analgesic pain reliever, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol, others).
Self-care therapies
With your drug treatment, your doctor will instruct you to use a self-care method called the Valsalva maneuver. To do this, you pinch your nostrils shut, close your mouth and gently force air into the back of your nose, as if you were blowing your nose. Once the medications have improved the function of the eustachian tubes, use of the Valsalva maneuver may force the tubes open.
Surgery
Surgical treatment of airplane ear is rarely necessary. However, your doctor may make an incision in your eardrum (myringotomy) to equalize air pressure and drain fluids.
Severe injuries, such as a ruptured eardrum or ruptured membranes of the inner ear, usually will heal on their own. However, in rare cases, surgery may be needed to repair them.
Preparing for your appointment
If you experience severe pain or symptoms associated with airplane ear that don't resolve with self-care techniques, you'll likely see your family doctor or a general practitioner first. You may, however, be referred to an ear, nose and throat (ENT) specialist. It's useful to prepare for your appointment.
What you can do
- Write down any symptoms you're experiencing, including any that may seem unrelated to your ear problems.
- Make a list of all medications, vitamins or supplements you're taking.
- Write down questions to ask your doctor.
Preparing a list of questions will help you make the most of your time with your doctor.
If you're experiencing signs or symptoms of airplane ear, you might want to ask the following questions:
- Are these signs and symptoms likely related to my recent airplane travel?
- What is the best treatment?
- Am I likely to have any long-term complications?
- How will we monitor for possible complications?
- How can I prevent this from happening again?
- Should I consider canceling travel plans?
- Are there brochures or other printed material I can take with me? What websites do you recommend?
Don't hesitate to ask your doctor any other questions you have.
What to expect from your doctor
Your doctor will ask you a number of questions, including:
- When did your symptoms begin?
- How severe are your symptoms?
- Do you have allergies?
- Have you had a cold, sinus infection or ear infection recently?
- Have you had airplane ear before?
- Were your past experiences with airplane ear prolonged or severe?
What you can do in the meantime
To treat pain, you may take a nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) or naproxen sodium (Aleve, others), or an analgesic pain reliever, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol, others).
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Are you a healthcare practitioner who enjoys patient education, interaction and communication?
If so, we invite you to criticise, contribute to or help improve our content. We find that many practicing doctors who regularly communicate with patients develop novel and often highly effective ways to convey complex medical information in a simplified, accurate and compassionate manner.
MedSquirrel is a shared knowledge, collective intelligence digital platform developed to share medical expertise between doctors and patients. We support collaboration, as opposed to competition, between all members of the healthcare profession and are striving towards the provision of peer reviewed, accurate and simplified medical information to patients. Please share your unique communication style, experience and insights with a wider audience of patients, as well as your colleagues, by contributing to our digital platform.
Your contribution will be credited to you and your name, practice and field of interest will be made visible to the world. (Contact us via the orange feed-back button on the right).
Disclaimer:
MedSquirrel is a shared knowledge, collective intelligence digital platform developed to share medical knowledge between doctors and patients. If you are a healthcare practitioner, we invite you to criticise, contribute or help improve our content. We support collaboration among all members of the healthcare profession since we strive for the provision of world-class, peer-reviewed, accurate and transparent medical information.
MedSquirrel should not be used for diagnosis, treatment or prescription. Always refer any questions about diagnosis, treatment or prescription to your Doctor.
